Secure by design: How open banking mitigates data breach impact
How to build a local payment strategy for global growth
Latin America’s digital wallet boom: What’s driving adoption in 2025
A merchant’s guide to transaction monitoring
How the UK pays: A merchant’s guide to the evolving payment landscape
A merchant’s guide to transaction monitoring
As digital payments continue to dominate global commerce, transaction monitoring has become a critical part of protecting businesses from fraud, chargebacks, and regulatory penalties. But what exactly does transaction monitoring involve, and how can merchants implement it effectively?
In this guide, we’ll walk you through the essentials of transaction monitoring, why it matters, how it works, and what to look for in a solution.
What is transaction monitoring?
Transaction monitoring refers to the process of reviewing and analysing financial transactions in real time or retrospectively to identify suspicious or unusual activity. For merchants, this is not just a compliance tool, it’s a defence against payment fraud, money laundering, and revenue loss.
Monitoring can detect a range of red flags, such as:
- Unusual transaction volumes
- Multiple failed payment attempts
- Rapid changes in customer behaviour
- Use of high-risk countries or IP addresses
- Mismatched cardholder information
Key use cases for transaction monitoring
Transaction monitoring plays a vital role across different industries and business models. While its applications vary, the core purpose remains the same: to protect the integrity of payments and reduce risk. Below are some of the most common use cases:
1. Anti-money laundering (AML)
For businesses operating in regulated sectors, especially those involved in cross-border transactions, monitoring is a critical AML tool. It helps identify suspicious patterns, such as smurfing (splitting transactions to avoid detection), rapid inflow or outflow of funds, or inconsistent customer behaviour. By flagging these anomalies, merchants can submit Suspicious Activity Reports (SARs) and stay compliant with financial crime regulations.
2. Fraud prevention
One of the most immediate applications is fraud detection. Transaction monitoring helps identify stolen card usage, friendly fraud, account takeovers, and bot activity. When paired with device fingerprinting and behavioural analytics, it can stop fraudulent transactions in real time, before damage is done.
3. Regulatory compliance
Payment service providers (PSPs), financial institutions, and merchants in regulated markets are required to comply with standards like PSD2 and GDPR. Transaction monitoring enables businesses to document their efforts to prevent financial crime, support audit processes, and demonstrate compliance in case of an investigation.
4. Cryptocurrency and virtual asset monitoring
Merchants and platforms dealing in digital assets must monitor crypto transactions for both fraud and regulatory purposes. This includes tracking wallet activity, flagging transactions that involve mixers or privacy coins, and detecting sudden spikes in volume or transfers to high-risk jurisdictions. With the rise of crypto adoption, transaction monitoring is crucial for meeting evolving global standards and protecting against crypto-specific threats.
How transaction monitoring works
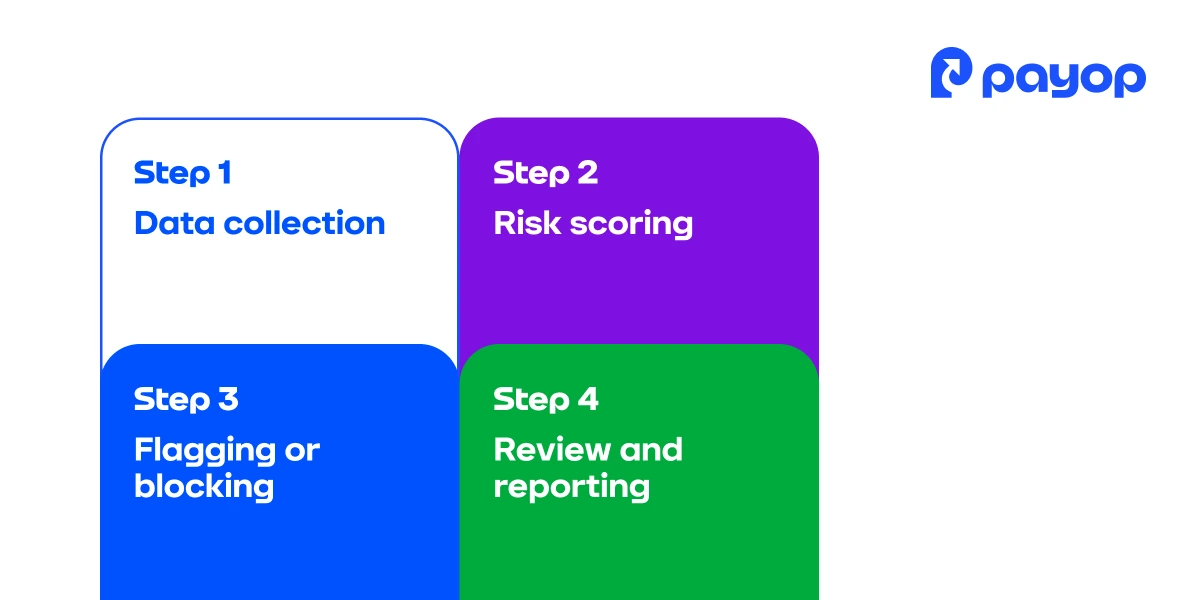
An effective transaction monitoring system operates through a combination of rule-based logic, machine learning, and human oversight. Here’s how it typically works behind the scenes:
Step 1: Data collection
When a transaction is initiated, the system collects details such as amount, currency, time, device fingerprint, customer profile, and geolocation.
Step 2: Risk scoring
Each transaction is analysed and assigned a risk score based on predefined rules and machine learning algorithms. Rules might include velocity checks, mismatches in billing and shipping addresses, or the use of a VPN.
Step 3: Flagging or blocking
Transactions deemed risky are either automatically declined, held for review, or routed through additional authentication steps, like 3DS.
Step 4: Review and reporting
The relevant department can manually review flagged transactions. Systems also generate reports for internal audits and regulatory purposes.
Learn how tokenisation improves transaction security.
Why businesses need transaction monitoring
Transaction monitoring is crucial for maintaining business security and compliance. Here’s why it matters for merchants:
- Fraud prevention: E-commerce fraud is a growing concern, especially with the rise of cross-border transactions. Monitoring tools help detect patterns that indicate stolen card use, account takeover, or bot-driven attacks.
- Chargeback reduction: A well-monitored transaction system can flag risky payments before they’re completed, helping prevent disputes that lead to costly chargebacks.
- Regulatory compliance: Depending on your region and industry, you’re likely required to follow anti-money laundering (AML) or Know Your Customer (KYC) regulations. Transaction monitoring is essential for staying compliant with frameworks like PSD2.
Business intelligence: Beyond fraud, analysing transaction patterns can help merchants understand customer behaviour, spot bottlenecks, and optimise their checkout flows.
How Payop supports merchants with transaction monitoring
At Payop, we understand how critical transaction monitoring is to merchant success. That’s why our platform includes built-in fraud detection tools and real-time alerts. Whether you run an e-commerce site, a gaming platform, or a digital marketplace, our system helps you:
- Reduce chargebacks
- Flag high-risk activity
- Comply with international standards
- Maintain trust with your customers
With Payop, there’s no need to choose between security and growth – you can have both.