How to prevent payment fraud: A step-by-step guide

- What is payment fraud?
- Types of payment fraud
- How to protect your business from payment fraud
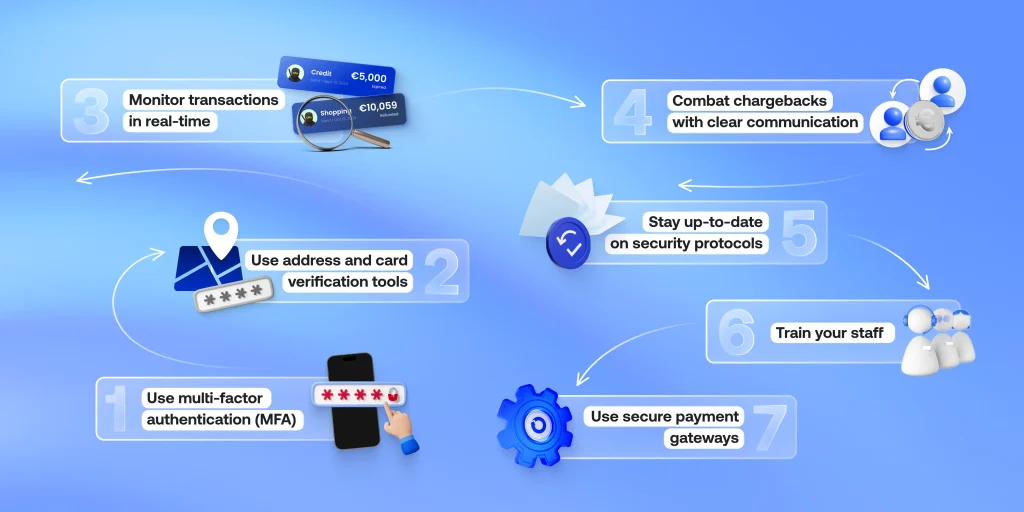
- Step 1: Use multi-factor authentication (MFA)
- Step 2: Use address and card verification tools
- Step 3: Monitor transactions in real-time
- Step 4: Combat chargebacks with clear communication
- Step 5: Stay up-to-date on security protocols
- Step 6: Train your staff
- Step 7: Use secure payment gateways
As online shopping grows, so does the risk of fraud. Cybercriminals are constantly evolving their tactics, and if you’re running an online business, you must stay one step ahead.
Protecting your business from payment fraud is more than just securing transactions – it’s about maintaining your reputation, safeguarding your customers, and ensuring the longevity of your business.
Let’s break down the types of fraud you might encounter and what steps you can take to keep your business safe.
What is payment fraud?
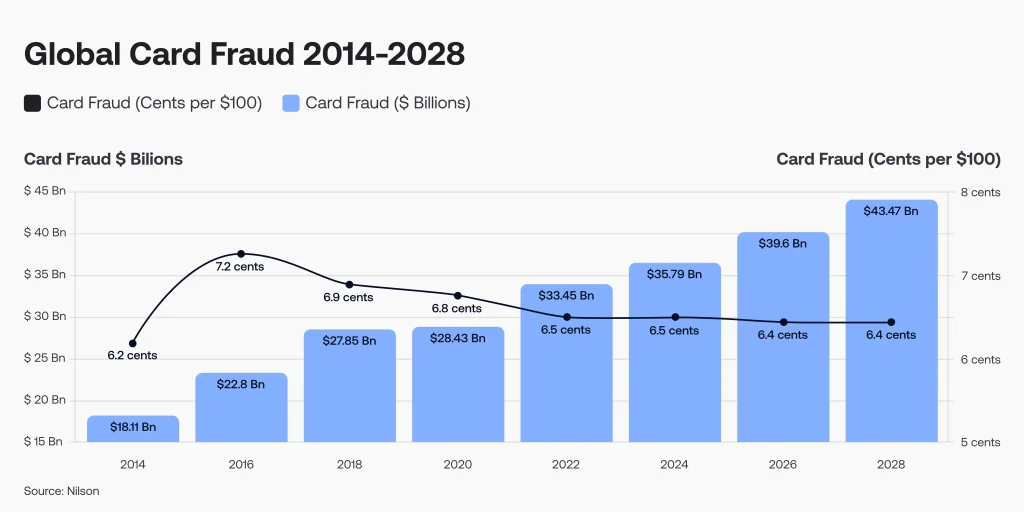
Payment fraud is the intentional use of false or stolen payment information to conduct unauthorised transactions. The goal is usually to steal money, goods, or services.
In 2023 80% of companies were victims of payment fraud. It can happen in many ways, such as using stolen credit card details, pretending to be someone else, or taking advantage of weak spots in payment systems. It can target both businesses and consumers, leading to financial losses, damaged reputations, and operational disruptions.
Types of payment fraud
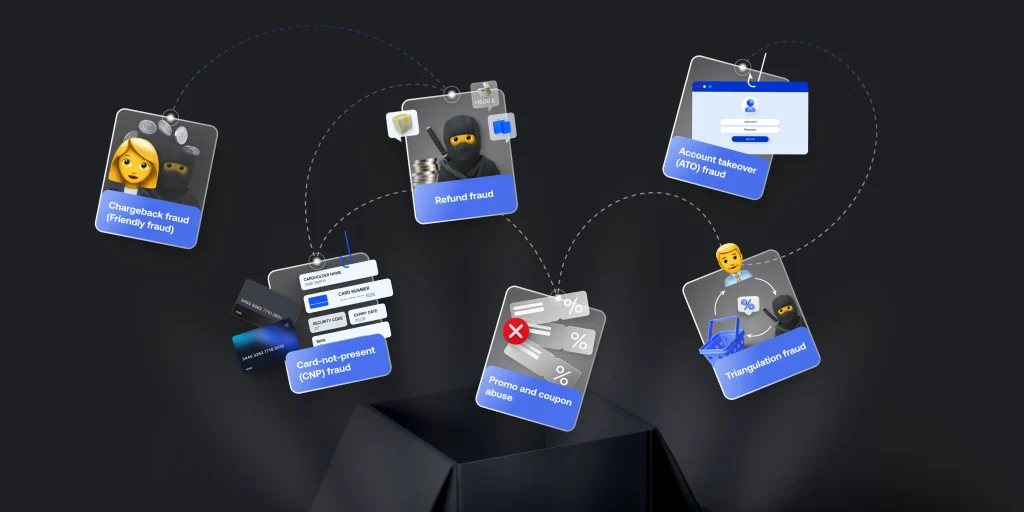
Online fraud comes in many forms, and as a merchant, being aware of these is half the battle. Here are some of the most common types you might face:
- Card-not-present (CNP) fraud: This is the classic online fraud scenario. Someone uses stolen credit card details to make purchases on your site without ever presenting a physical card.
- Chargeback fraud (Friendly fraud): A customer buys something and receives it but then disputes the charge with their bank, claiming they never got it. This leaves you out of the product and the payment.
- Account takeover (ATO) fraud: A fraudster gets access to a legitimate customer’s account (often via phishing or hacking) and makes unauthorised purchases using stored payment details.
- Refund fraud: The scammer claims they didn’t receive their order or that it was faulty, demanding a refund or replacement when in reality, everything was fine.
- Promo and coupon abuse: Fraudsters exploit your discounts and promo codes by creating fake accounts or abusing loopholes to get items at an unfairly low price.
- Synthetic identity fraud involves creating fake identities using a mix of real and fabricated information. These identities are used to open fraudulent accounts and rack up charges.
- Triangulation fraud: In this scheme, fraudsters act as middlemen. They sell products they don’t own at a discount, take payments from legitimate buyers, and use stolen card details to purchase the items from your site.
How to protect your business from payment fraud
Now that you understand the landscape of payment fraud let’s dive into how you can protect your business from these threats.
Step 1: Use multi-factor authentication (MFA)
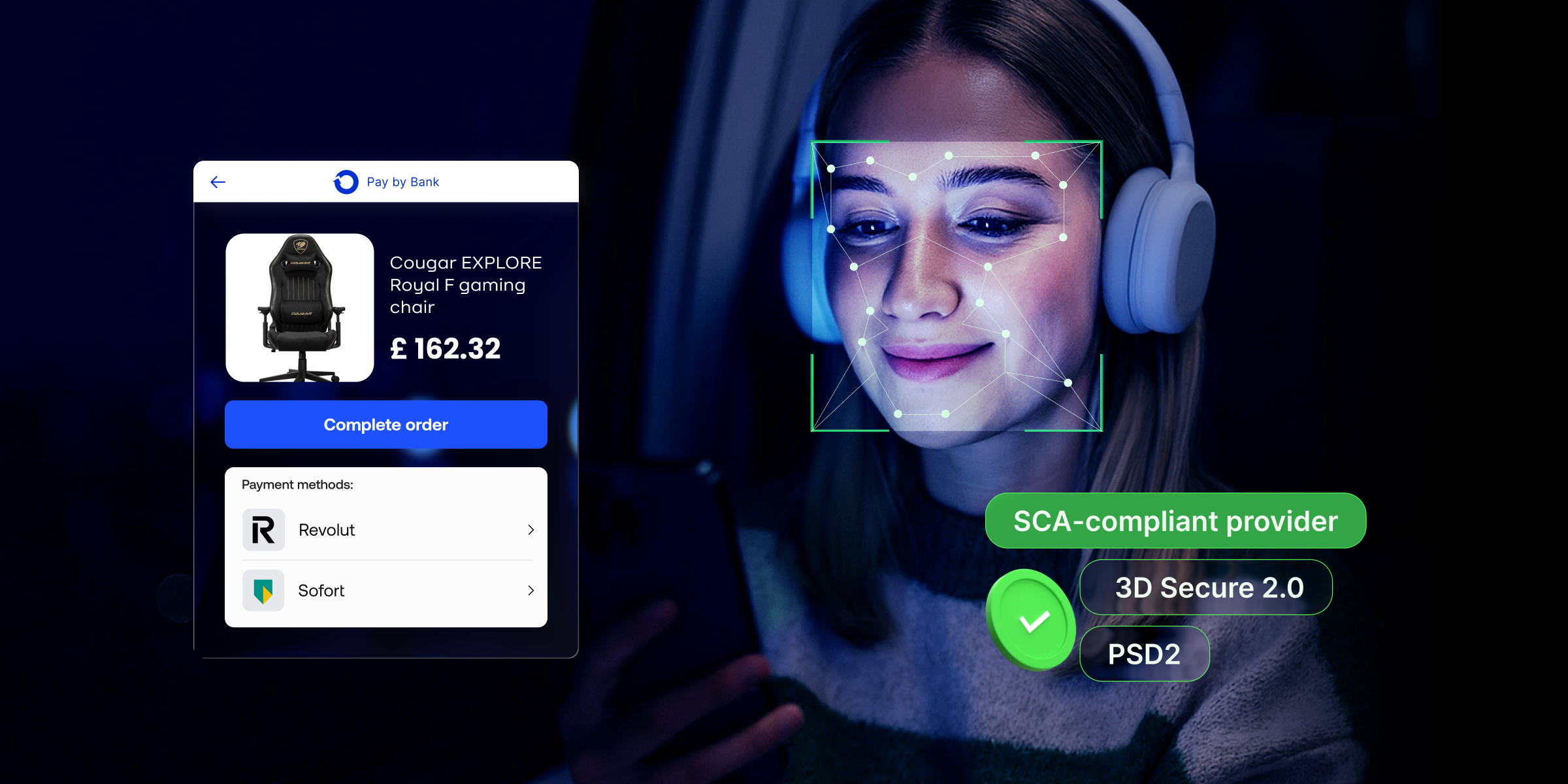
Implementing MFA is an easy way to increase security for both your customers and your staff. It requires users to verify their identity through something they know (like a password), something they have (like a phone), or something they are (like a fingerprint). This extra layer makes it much harder for fraudsters to break in.
- For customers: Encourage MFA for login and high-value transactions. It’s a minor inconvenience that significantly enhances security.
- For staff: Admins with access to customer data should always use MFA to protect your internal systems. The same goes for the payment provider. At Payop, the use of 2FA is a mandatory procedure for both employees and merchants.
Learn how open banking protects users’ data.
Step 2: Use address and card verification tools
Payment fraud prevention starts before the transaction even goes through. Implementing Address Verification Systems (AVS) and Card Verification Value (CVV) checks can help:
- AVS compares the customer’s billing address with the one their credit card issuer provided. If the addresses don’t match, it’s a red flag.
- CVV requires the customer to enter the three- or four-digit code from the back of the card, ensuring they physically possess it.
Step 3: Monitor transactions in real-time
Fraud detection software can help you spot unusual patterns before they cause damage. Here’s what to watch for:
- Unusually large orders: A sudden spike in order value could indicate fraud.
- Multiple orders from one IP address: This could be a sign of a bot or scam, especially if they’re for different customers.
- Different billing and shipping addresses: While this isn’t always a red flag, it’s worth double-checking, especially for expensive orders.
By setting up real-time alerts, you can quickly investigate suspicious activities and prevent payment fraud before it happens. However, by partnering with Payop, you can rely on our anti-fraud tools and focus on growing your business without spreading your resources on security issues.
Step 4: Combat chargebacks with clear communication
Chargebacks can be a serious headache for merchants, but many are preventable with clear communication:
- Detailed product descriptions: Ensure your product listings are clear and accurate to avoid misunderstandings.
- Transparent return policies: Make sure your return policies are easy to find and understand to reduce the chances of disputes.
- Order confirmation and shipping notices: Keep your customers informed at every stage of the process. This gives them peace of mind and gives you proof of delivery in case of disputes.
When chargebacks happen, respond quickly and provide any necessary documentation to resolve the issue in your favour.
Step 5: Stay up-to-date on security protocols
Cyber threats evolve, so keeping your systems updated is essential to protecting your business:
- SSL encryption: Ensure your website has an SSL certificate, which encrypts sensitive data like payment details.
- PCI compliance: Adhere to Payment Card Industry Data Security Standards (PCI DSS) to ensure you’re handling credit card data responsibly.
- Regular software updates: Make sure your payment gateways and security software are always up to date.
Step 6: Train your staff
Your staff plays a crucial role in preventing payment fraud. Regular training helps them spot suspicious activities and handle sensitive data securely:
- Phishing awareness: Teach your employees to recognise phishing scams that might target your business, such as fake refund requests or suspicious emails.
- Data handling: Ensure your team knows how to securely handle and store customer data to prevent breaches.
- Recognising red flags: Empower your team to flag suspicious transactions or customer behaviour, such as unusually large orders or requests for multiple shipping addresses.
Step 7: Use secure payment gateways
Choosing the right payment gateway is a crucial decision for merchants. Reputable gateways come with built-in fraud prevention features like:
- Tokenization: Instead of storing sensitive payment data, tokenization replaces it with a unique code that’s meaningless if stolen.
- Encryption: Payment details are encrypted during the transaction, ensuring they can’t be intercepted.
- Customisable fraud filters: Many gateways allow you to set filters that block high-risk transactions based on criteria like geography, amount, or number of transactions in a given time frame.
Payop offers much more than just basic payment processing – it’s a smart, proactive shield for your business. With Payop, you get access to a global payment platform designed to protect you at every step of the transaction process.
Imagine having a partner who watches over your transactions in real time, identifying and stopping suspicious activities before they harm your business. That’s Payop. With our platform, security doesn’t slow you down; it empowers your growth while building trust with your customers.Contact our team at sales@payop.com to learn more.