Understanding open banking: A comprehensive guide

If you use payment or financial services and apps, you are probably at least relatively familiar with open banking. Its essence lies in the secure exchange of financial information with third-party providers to enable users to manage their finances in a more efficient and versatile way. But what does it actually mean, and how is it technically possible? And the most frequently asked question: is it really safe?
In this concise but informative blog, we will answer these questions and break down the concept of open banking point by point.
What is open banking?
Let’s start with the basics – the definition of open banking. It’s a data-sharing concept that allows third-party financial service providers to access a user’s financial information from traditional banks through secure APIs. This typically involves account information, transaction histories, and other financial details.
One more definition before we proceed. API or application programming interface is a technological bridge of a kind that simplifies communication between different software systems or applications. They act as gateways, ensuring data transmission occurs securely and with the user’s explicit consent. In the context of open banking, APIs allow banks and other financial institutions to securely share specific financial data with authorised third-party providers.
Simply put, thanks to this concept, non-banking organisations can perform banking tasks.
How does open banking work?
Again, everything starts with data sharing. Individuals can grant specific access permissions to their financial data at their discretion through secure channels. Utilising this information, third-party providers can offer various services. For instance, they can analyse the customers’ accounts and transaction history to present diverse financial service options tailored to their economic behaviour and needs.
However, one of the most significant features of the open banking API is the ability to initiate new transactions or account changes on behalf of a customer. This feature ensures smooth financial interactions and transactions, allowing customers to use services and products offered by third-party providers without switching between multiple platforms or institutions.
Read our comprehensive guide to payment processing.
Benefits of open banking for consumers
The advantages for consumers resulting from open banking are wide-ranging. The most significant benefits are:
- the ability to access various accounts from a single platform or app, which makes financial planning and decision-making easier by providing a full view of income, expenses and savings;
- development of personalised financial services and products;
- the possibility of obtaining fast loans, thanks to the consolidation of all financial history;
- availability of a broad range of payment methods such as credit cards, “buy now – pay later”, etc;
- and the overall increased convenience of online shopping, money transfers and currency conversion.
Benefits of open banking for businesses
Businesses, too, find open banking to be advantageous. This system creates a favourable environment for innovation in the financial sector. Startups and established financial service providers can develop new, innovative products and services more efficiently, thanks to access to a broader pool of financial data and APIs from various banks.
Moreover, businesses benefit from additional financial services, such as improved cash flow management tools, optimised payment processing solutions, and easier access to loans or credits. The competition that open banking creates encourages financial institutions to offer more favourable terms and services, which ultimately benefits businesses looking for financial solutions.
Regulatory landscape
The implementation of Open Banking has its regulatory framework. Various regions have established guidelines and standards to ensure the security, privacy, and fair usage of financial data.
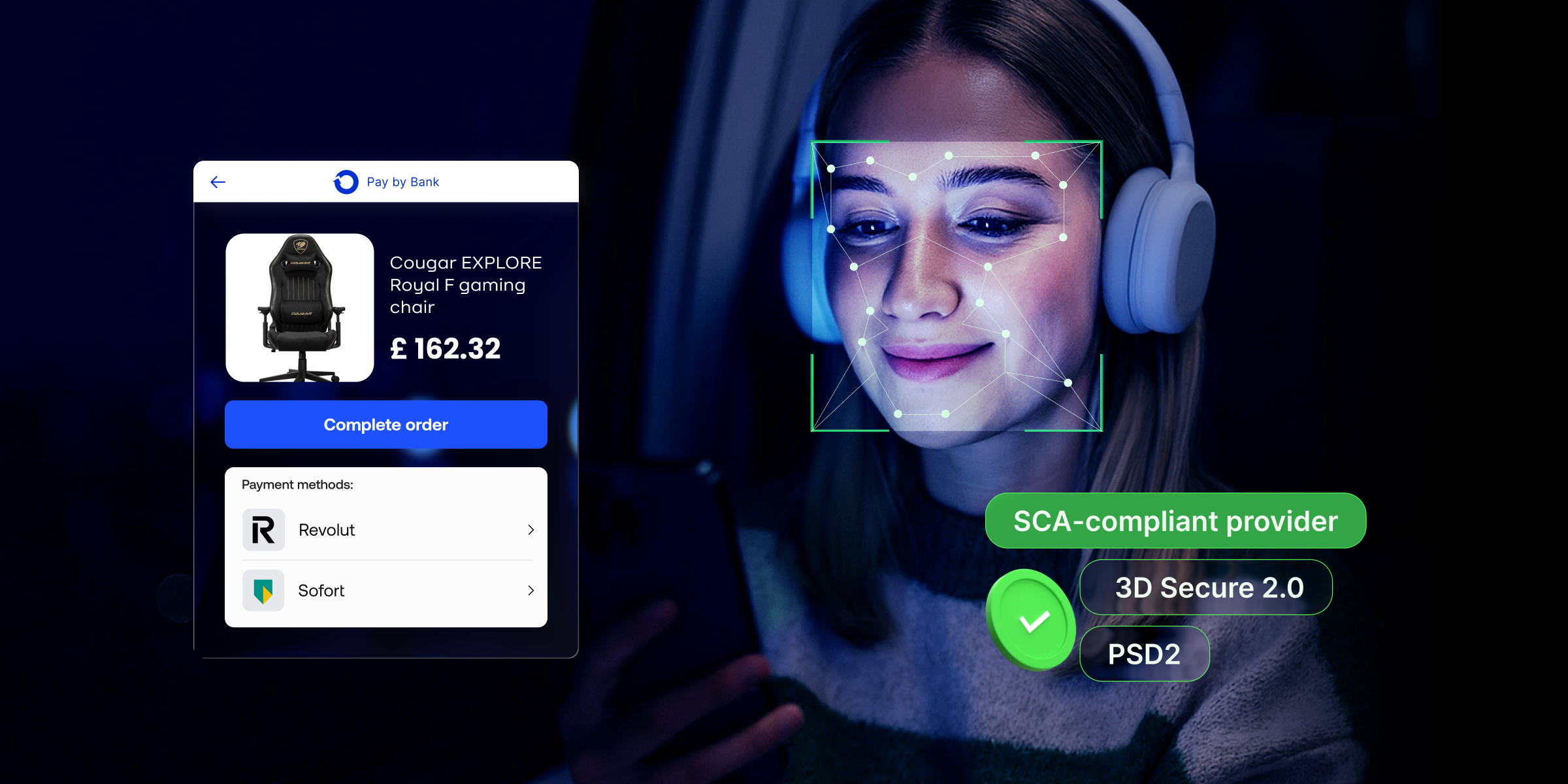
In Europe a cornerstone of open banking regulations is PSD2 (Payment Services Directive 2). It compels banks to open up their APIs, allowing third-party providers secure access to account information and enabling them to initiate payments on behalf of customers. It not only aims to enhance competition and innovation but also prioritises consumer protection and data security within the payment services sector.
You can learn more about PSD2 and its security aspects in this article.
Conclusion
In just a few years, open banking has fundamentally changed the way we think about financial services. Like many technologies, this one aims to simplify, speed up and optimise our lives by making it easier to access and manage money. In addition, it opens the door to personalised advice, innovative products and various financial services. Embracing this evolution, being informed and actively participating in the transformational process is key to unlocking the full potential of open banking for a smarter and more accessible financial future.